 |
 |
| Korean J Ophthalmol > Volume 25(1); 2011 > Article |
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate factors responsible for the variability between intended and achieved corneal-flap thickness during femtosecond laser-assisted laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK).
Methods
A prospective, nonrandomized, case study was performed on 35 eyes of 18 consecutive patients who underwent LASIK surgery using the 60 kHz femtosecond laser microkeratome. Eyes were assigned to three different thickness groups, with 110-, 120-, or 130-Āµm cut depths. Anterior segment optical coherence tomography was used to assess the morphology of 35 LASIK flaps at postoperative one week postoperatively. The flap thickness was assessed at seven measuring points across each flap. Patient age, preoperative spherical equivalent, manual keratometry, preoperative central pachymetry, and regional variability of the cornea were evaluated to determine where they influenced the achieved corneal flap thickness.
Results
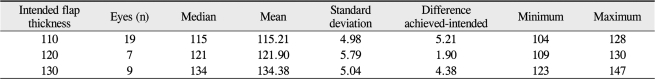
Cuttings of all flaps were easily performed without any intraoperative complications. Flap-thickness measurements had a mean of 115.21 Ā± 4.98 Āµm (intended thickness, 110 Āµm), 121.90 Ā± 5.79 Āµm (intended, 120 Āµm), and 134.38 Ā± 5.04 Āµm (intended, 130 Āµm), respectively. There was no significant difference between the 110-Āµm and 120-Āµm groups when compared with the 130-Āµm group (one-way analysis of variance test, p > 0.05). Patients' age, preoperative spherical equivalent, manual keratometry, and preoperative central pachymetry did not affect the achieved flap thickness (Pearson correlations test, p > 0.05). The reproducibility of flap thickness in the central 1.5-mm radius area was more accurate than that in the peripheral 3.0 to 4.0-mm radius area (paired samples t-test, p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Femtosecond laser-assisted LASIK is likely to reproduce a reliable thickness of the corneal flap, which is independent of corneal shape factors or refractive status. Future studies should focus on variations in corneal biomechanical factors, which may also play an important role in determining flap thickness.
Over the past decade, laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) has become the most common refractive procedure for the correction of refractive errors. Consistency and predictability of corneal flap thickness is crucial in both planning and in producing successful LASIK outcomes. Complications associated with thin flaps include flap slippage, striae, irregularity, astigmatism, buttonholes, free caps, and corneal haze. Thicker flaps cause decreased stromal-bed thickness, which increases the risk for biomechanical corneal changes and iatrogenic corneal ectasia [1-4].
Few studies have attempted to find a correlation between preoperative variables and corneal-flap thickness with the mechanical microkeratome. Yildirim et al. [5] found a low correlation with preoperative corneal thickness and no correlation with preoperative keratometry when using the mechanical microkeratome. Giledi et al. [6] reported a correlation between preoperative spherical-equivalent refraction and flap thickness, and a paradoxical finding of thinner flaps in patients with thicker corneas using the mechanical microkeratome. Current mechanical microkeratomes have a very good performance record; however, in a few cases, complications can occur during the microkeratome pass and flap cut. Femtosecond lasers offer an alternative to mechanical cutting and can provide additional features that affect flap morphology. Studies by Krueger and Dupps [7] and AliĆ³ and PiƱero [8] found a planar-flap profile for femtosecond-laser-created flaps versus a meniscus-flap profile for microkeratome flaps. A meniscus flap extends deeper in the periphery and is shallower in the center of the flap, while a planar flap has the same thickness across its entirety. Despite the improved flap-thickness predictability with the femtosecond lasers compared with the conventional microkeratome, unexpectedly thinner or thicker flaps sometimes occur with the femtosecond lasers and can lead to surgical complications [9]. The main aim of this study was to evaluate preoperative variables and flap thickness in eyes having flap creation with the femtosecond-laser-assisted LASIK.
This prospective study included patients who had uneventful LASIK for myopia between November 2008 and Feburary 2009. The flap was created with a 60 kHz femtosecond laser (IntraLase; Abbott Medical Optics, Irvine, CA, USA). All patients had a full preoperative workup including topography (Orbscan; Bausch & Lomb, Rochester, NY, USA), and pachymetry. No patient had corneal abnormalities or contraindications to LASIK. All patients provided written informed consent.
The patients were divided into three groups. In 110-Āµm group, the intended corneal-flap thickness was 110 Āµm. The targeted corneal flap thickness was 120 Āµm for 120-Āµm group. 130-Āµm group, the intended corneal-flap thickness was 130 Āµm.
The same surgeon (CKJ) performed all the LASIK procedures. The femtosecond laser was programmed to a flap thickness of 110 Āµm to 130 Āµm and a flap diameter of 8.3 mm to 9.0 mm with a 90-degree angled side cut and a 55-degree hinge angle. The femtosecond laser's bed energy was 0.65 mJ, it's side cut energy was 0.8 mJ and it's repetition frequency was 60 kHz. The myopic stromal ablations were performed with a Visx Star S4 excimer laser (Wavescan; VISX, Sunnyvale, CA, USA).
Imaging and measurement of the LASIK flaps were performed by high-speed AS-optical coherence tomography (OCT) (Visante; Carl Zeiss-Meditec, Dublin, CA, USA). This noncontact system generates images of the complete flap cross-section with precise geometry and reduces movement artifacts and distortion [10,11]. Imaging is performed with the patient seated, and cross-sectional images of the anterior chamber and the cornea are generated. A horizontal OCT image of the cornea was taken by the same experienced examiner (YJL) at one week after surgery. The imaging and measurements were repeated three times per patient. Flap thickness was measured at seven points in each horizontal image (center, Ā±1.5 mm, Ā±3.0 mm, Ā±4.0 mm to the vertex) (Fig. 1).
Patients were examined before LASIK and also one week and one month after surgery. At each visit, the uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA) and best corrected visual acuity were measured using the Snellen visual-acuity test. Postoperative topical medication regimens were identical in all groups and consisted of gatifloxacin ophthalmic solution, diclofenac ophthalmic solution and fluorometholon 0.1% four times a day for seven days and then tapered over the next week.
The correlations between preoperative variables and corneal-flap thickness were analyzed using Pearson correlation statistics. A one-way analysis of variance test was used to compare differences in flap thickness among 110-Āµm, 120-Āµm and 130-Āµm groups. Data were analyzed using the Excel XP program (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) and the SPSS ver. 13.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). A p-value of 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
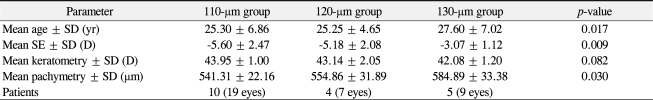
This prospective study included 35 eyes of 18 patients (5 males, 13 females) with a mean age of 26.20 Ā± 6.30 years (standard deviation, SD) (range, 19.0 to 40.0 years). The mean preoperative spherical equivalent (SE) was -4.86 Ā± 2.34 diopters (D). The mean preoperative corneal keratometry was 43.31 Ā± 1.50 D, and the mean preoperative corneal pachymetry on ultrasound was 557.40 Ā± 31.05 mm. Table 1 shows the preoperative demographics of the patients.
Increasing the intended thickness by 10-mm increments increased the mean achieved thickness (Fig. 2). In addition, the mean achieved thickness exceeded the intended thickness by 1 Āµm to 6 Āµm (Table 2). We verified the correlation between the intended corneal-flap thickness and the achieved corneal flap thickness. There was no significant difference between the 110-Āµm and 120-Āµm groups when compared with the 130-Āµm group (one-way ANOVA test, p > 0.05).
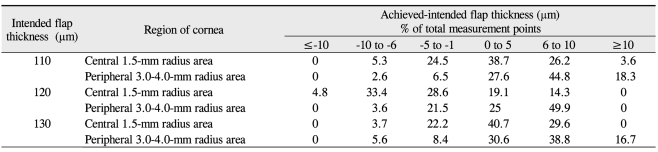
The periphery of the flaps showed higher variations in thickness and deviations from the intended flap thickness (Table 4). The mean achieved flap thickness in the central 1.5 mm radius area was thicker than that in the peripheral 3.0 to 4.0-mm radius area (paired-samples t-test; 110-Āµm group, p = 0.001; 120-Āµm group, p = 0.004; 130-Āµm group, p = 0.014) (Table 5 and Fig. 3).
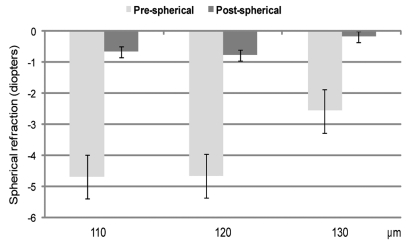
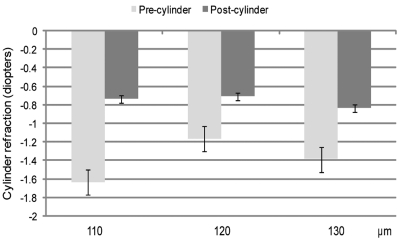
Figs. 4-6 show the UCVA and spherical and cylinder refraction preoperatively and one month postoperatively. There were good visual outcomes in all groups, and there was no significant difference among any group for refractive error. No sight-threatening intraoperative or postoperative complications waere seen. No infection was noted.
Since the initial LASIK procedures were performed in 1990 [12], multiple mechanical microkeratomes have been used to create the corneal flap [13-21]. The current microkeratomes have a very precise and reliable performance and show standard deviations in flap thickness between 15 and 35 Āµm [22]. However, the accuracy of mechanical microkeratomes is due to their specifications, and their method of cutting is limited. Therefore, they still can cause some complications during the cutting process. Among these are incomplete cuts, free caps, off centered flaps, button holes, inconsistent flap thickness, epithelial defects, induction of higher-order corneal aberrations, etc. [23,24]. A different approach to cutting corneal flaps is the use of laser energy. Ultrashort laser pulses such as those emitted by pico- and femtosecond lasers, have been tested, and femtosecond laser technology has shown the most promising results in flap separation [25]. The femtosecond laser is a focusable infrared laser, which uses pulses in the femtosecond (10-15 s) duration range. Contiguous pulses are placed at a precise depth within the cornea. The 1,053-nm wavelength of light used by the laser is transparent to the cornea, so it resects only targeted tissue while leaving the surrounding tissue unaltered. Because the energy and firing patterns are controlled by a computer, the laser is capable of cutting tissue at various depths and patterns, which produces minimal inflammation or collateral tissue damage [26-29]. Thermal damage to adjacent tissue in the cornea has been measured to be in a 1-mm radius [30]. The laser essentially vaporizes small volumes of tissue by photodisruption, producing plasma, a shock wave, cavitation, and gas (CO2 and H2O) bubbles. The femtosecond laser creates a resection plane for a lamellar cut using a spot size of 2.5 mm, a pulse-repetition rate of 15 to 60 kHz and a pulse width of 600 to 800 femtoseconds. The intensity of the laser energy can be varied at the operator's discretion. A side (trephination) cut can also be fashioned from the stroma to the surface of the cornea for anterior flaps in LASIK. The cut angle can be varied between 45Ā° and 90Ā°. The femtosecond laser is also capable of creating lamellar dissections ranging from 5 mm to 9.5 mm in diameter.
The femtosecond laser's range of achieved flap thickness is narrower than that created with conventional microkeratomes. This advantage translates into few thicker-than-expected flaps, which reduces the risk for ectasia, and very few thinner flaps, which reduces the risk for cap perforation and corneal striae. Mechanical microkeratomes tend to create meniscus-shaped corneal flaps that are thinner in the center and thicker in the periphery, whereas the femtosecond laser typically creates a more uniform planar flap. AliĆ³ and PiƱero [8] found that the peripheral pachymetric values of the Moria M2 microkeratome flaps were always higher than those corresponding with the IntraLase flap.
The femtosecond laser is not perfect. Unexpectedly thinner or thicker flaps sometimes occur with the femtosecond laser and can lead to surgical complications [9]. Flap thickness has been an important measure of femtosecond-assisted LASIK safety. Pfaeffl et al. [31] found that the following factors had a low correlation with preoperative keratometry in predicting the variance of the achieved flap thickness, selection of the right suction ring, suction time, use of the pocket option, flap diameter, temperature, and humidity when using the femtosecond laser microkeratome. Binder [32] suggested that the femtosecond laser photodisrupts more deeply when set between 110 Āµm and 120 Āµm with an SD of 12 Āµm but dissects less deeply when set between 130 Āµm and 140 Āµm with an SD of 18.5 Āµm. Sutton and Hodge [33] reported no significant correlation in either group between keratometry and flap thickness, or between preoperative pachymetry and flap thickness. Additionally, 74.9% of patients treated with 15 kHz had a corneal flap within 20 Āµm of the intended location, which was increased to 97.9% with the 30-kHz laser [33].
In this study, the intended flap thickness was 110, 120 or 130 Āµm depending on the surgeon's preference. One week posteratively, the mean achieved flap thickness was 115.21 Ā± 4.98 Āµm (range, 104 to 128 Āµm) in the 110-Āµm group, 121.90 Ā± 5.79 Āµm (range, 109 to 130 Āµm) in the 120-Āµm group and 134.38 Ā± 5.04 Āµm (range, 123 to 147 Āµm) in the 130-Āµm group. There was no significant difference between the 110-Āµm and the 120-Āµm groups when compared with the 130-Āµm group. No significant correlations were found between the residual of the achieved flap thickness and age, preoperative keratometry, pachymetry, or SE. In our study, the periphery of the flap showed higher variations in thickness and greater deviations from the intended flap thickness. The mean achieved flap thickness in the central 1.5-mm radius area was thicker than that in the peripheral 3.0 to 4.0-mm radius area. The difference of the mean achieved-flap thickness between the central and peripheral areas ranged from 3.33 Āµm to 5.58 Āµm (Table 5). Li et al. [34] reported that the repeatability of OCT corneal-thickness measurements was 2 Āµm. Other studies found that the mean femtosecond laser flap thickness increased slightly toward the periphery [35].
The possible factor is the biomechanical characteristics of the cornea. Dawson et al. [36] reported a difference in tensile strength between the central and peripheral cornea, with increasing tensile strength moving from the center to the periphery. However, when boundaries between the corneal flap and the stroma become ambiguous, especially in the central portion of the cornea, corneal-flap thickness measurements using OCT are not absolutely precise.
In conclusion, the ultimate goal of LASIK surgery is to provide patients with the best possible visual and refractive outcomes with the lowest risk of complications. Therefore flap thickness is an important indicator of LASIK safety because of the importance of stromal preservation. Sub-Bowman keratomileusis (SBK) is becoming a prominent procedure because SBK is said to combine the advantages of LASIK (i.e., low risk for haze and almost no pain) and classic photo-refractive keratectomy in the hopes of maintaining better corneal strength. However, these newer excimer laser techniques still have disadvantages caused by an unstable corneal flap. Further randomized studies are required to evaluate factors affecting flap thickness.
REFERENCES
1. Choudhri SA, Feigenbaum SK, Pepose JS. Factors predictive of LASIK flap thickness with the Hansatome zero compression microkeratome. J Refract Surg 2005;21:253-259.


2. Seiler T, Quurke AW. Iatrogenic keratectasia after LASIK in a case of forme fruste keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg 1998;24:1007-1009.


3. Seiler T, Koufala K, Richter G. Iatrogenic keratectasia after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Refract Surg 1998;14:312-317.


5. Yildirim R, Aras C, Ozdamar A, et al. Reproducibility of corneal flap thickness in laser in situ keratomileusis using the Hansatome microkeratome. J Cataract Refract Surg 2000;26:1729-1732.


6. Giledi O, Mulhern MG, Espinosa M, et al. Reproducibility of LASIK flap thickness using the Hansatome microkeratome. J Cataract Refract Surg 2004;30:1031-1037.


7. Krueger RR, Dupps WJ Jr. Biomechanical effects of femtosecond and microkeratome-based flap creation: prospective contralateral examination of two patients. J Refract Surg 2007;23:800-807.


8. AliĆ³ JL, PiƱero DP. Very high-frequency digital ultrasound measurement of the LASIK flap thickness profile using the IntraLase femtosecond laser and M2 and Carriazo-Pendular microkeratomes. J Refract Surg 2008;24:12-23.


9. Choi SK, Kim JH, Lee D, et al. Creation of an extremely thin flap using IntraLase femtosecond laser. J Cataract Refract Surg 2008;34:864-867.


10. Kohnen T, Thomala MC, Cichocki M, Strenger A. Internal anterior chamber diameter using optical coherence tomography compared with white-to-white distances using automated measurements. J Cataract Refract Surg 2006;32:1809-1813.


11. Li Y, Netto MV, Shekhar R, et al. A longitudinal study of LASIK flap and stromal thickness with high-speed optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2007;114:1124-1132.


12. Pallikaris IG, Papatzanaki ME, Stathi EZ, et al. Laser in situ keratomileusis. Lasers Surg Med 1990;10:463-468.


13. Behrens A, Langenbucher A, Kus MM, et al. Experimental evaluation of two current-generation automated microkeratomes: the Hansatome and the Supratome. Am J Ophthalmol 2000;129:59-67.


14. Sarkisian KA, Petrov AA. Experience with the Nidek MK-2000 microkeratome in 1,220 cases. J Refract Surg 2001;17(2 Suppl):S252-S254.


15. Choi YI, Park SJ, Song BJ. Corneal flap dimensions in laser in situ keratomileusis using the innovatome automatic microkeratome. Korean J Ophthalmol 2000;14:7-11.


16. Shemesh G, Dotan G, Lipshitz I. Predictability of corneal flap thickness in laser in situ keratomileusis using three different microkeratomes. J Refract Surg 2002;18(3 Suppl):S347-S351.


17. Spadea L, Cerrone L, Necozione S, Balestrazzi E. Flap measurements with the Hansatome microkeratome. J Refract Surg 2002;18:149-154.


18. Arbelaez MC. Nidek MK 2000 microkeratome clinical evaluation. J Refract Surg 2002;18(3 Suppl):S357-S360.


19. Flanagan GW, Binder PS. Precision of flap measurements for laser in situ keratomileusis in 4428 eyes. J Refract Surg 2003;19:113-123.


20. Solomon KD, Donnenfeld E, Sandoval HP, et al. Flap thickness accuracy: comparison of 6 microkeratome models. J Cataract Refract Surg 2004;30:964-977.


21. Duffey RJ. Thin flap laser in situ keratomileusis: flap dimensions with the Moria LSK-One manual microkeratome using the 100-microm head. J Cataract Refract Surg 2005;31:1159-1162.


22. Solomon KD, Donnenfeld E, Sandoval HP, et al. Flap thickness accuracy: comparison of 6 microkeratome models. J Cataract Refract Surg 2004;30:964-977.


23. Holzer MP, Vargas LG, Sandoval HP, et al. Corneal flap complications in refractive surgery. Part 1: development of an experimental animal model. J Cataract Refract Surg 2003;29:795-802.


24. AmbrĆ³sio R Jr, Wilson SE. Complications of laser in situ keratomileusis: etiology, prevention, and treatment. J Refract Surg 2001;17:350-379.


25. Kurtz RM, Horvath C, Liu HH, et al. Lamellar refractive surgery with scanned intrastromal picosecond and femtosecond laser pulses in animal eyes. J Refract Surg 1998;14:541-548.


26. Sarayba MA, Juhasz T, Chuck RS, et al. Femtosecond laser posterior lamellar keratoplasty: a laboratory model. Cornea 2005;24:328-333.


27. Soong HK, Mian S, Abbasi O, Juhasz T. Femtosecond laser-assisted posterior lamellar keratoplasty: initial studies of surgical technique in eye bank eyes. Ophthalmology 2005;112:44-49.


28. Seitz B, Langenbucher A, Hofmann-Rummelt C, et al. Nonmechanical posterior lamellar keratoplasty using the femtosecond laser (femto-plak) for corneal endothelial decompensation. Am J Ophthalmol 2003;136:769-772.


29. Seitz B, BrĆ¼nner H, Viestenz A, et al. Inverse mushroom-shaped nonmechanical penetrating keratoplasty using a femtosecond laser. Am J Ophthalmol 2005;139:941-944.


30. Jonas JB, Vossmerbaeumer U. Femtosecond laser penetrating keratoplasty with conical incisions and positional spikes. J Refract Surg 2004;20:397

31. Pfaeffl WA, Kunze M, Zenk U, et al. Predictive factors of femtosecond laser flap thickness measured by online optical coherence pachymetry subtraction in sub-Bowman keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg 2008;34:1872-1880.


32. Binder PS. Flap dimensions created with the IntraLase FS laser. J Cataract Refract Surg 2004;30:26-32.


33. Sutton G, Hodge C. Accuracy and precision of LASIK flap thickness using the IntraLase femtosecond laser in 1000 consecutive cases. J Refract Surg 2008;24:802-806.


34. Li Y, Shekhar R, Huang D. Corneal pachymetry mapping with high-speed optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2006;113:792-9.e2



Fig.Ā 1
Example of a horizontal cross-sectional optical coherence tomography image of the cornea. The calipers are located at the seven measurement points.

Fig.Ā 2
Increasing the intended thickness by 10-Āµm increments increased the mean achieved thickness. The mean achieved flap thickness in the central 1.5-mm radius area was thicker than that in the peripheral 3.0 to 4.0-mm radius area.
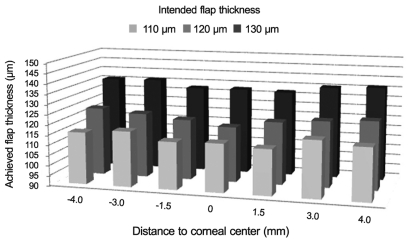
Fig.Ā 3
Correlation of achieved flap thickness and age, preoperative spherical equivalent, keratometry, and pachymetry.

TableĀ 2
Detailed results of thickness measurements for the three investigated flap thickness groups (Āµm)
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles
-
Lamina Cribrosa Changes after Laser
In Situ Keratomileusis in Myopic Eyes2018 April;32(2)






 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print