 |
 |
| Korean J Ophthalmol > Volume 23(1); 2009 > Article |
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the refractive predictability of a partial coherence interferometry (PCI) biometry device (IOL Master®) for cataract surgery and to investigate factors that may affect it.
Methods
Retrospective review of 209 eyes from 151 patients that had undergone preoperative PCI biometry and an uneventful phacoemulsification cataract surgery with posterior chamber intraocular lens (IOL) implantation was conducted. Prediction error defined as the intended refraction minus the postoperative refraction in spherical equivalent (SE) and the absolute error were analyzed according to IOL calculation formulas, patient characteristics, preoperative visual acuity (VA) and refraction, posterior subcapsular cataract (PSC), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and axial length (AL).
Results
The overall refractive predictability of the PCI device was good. Generally, the SRK/T formula performed better than the SRK-II formula. Refractive predictability was slightly worse in eyes with Ōēź+2.0 diopters (D) of preoperative SE (with both SRK-II and SRK/T) and in eyes with an ALŌēż23.0 mm (only with SRK-II. No other factors significantly affected the refractive predictability of the PCI, although poor VA, dense PSC, and poor SNR were closely interrelated.
Conclusions
The SRK/T formula performed significantly better than the SRK-II formula. Eyes with an ALŌēż23.0 mm were associated with significantly greater hyperopic shifts in postoperative refraction with the SRK-II formula, but not with the SRK/T formula. A preoperative SEŌēź+2.0D was related to a significantly greater hyperopic shift in postoperative refraction. With proper verification of measured data and a suitable IOL calculation formula, good refractive predictability is expected from PCI biometry regardless of patient characteristics, preoperative VA, SNR, PSC, and AL.
Since Harold Ridley implanted the first intraocular lens (IOL) into a blind eye and found a surprising refractive error of -20 diopters (D) in 1949, there have been many efforts made toward the precise prediction of refractive status following cataract surgery. With improvements in surgical techniques and innovations in the materials and designs of IOLs, patient expectations have also steadily increased significantly. Accuracy in the prediction of postoperative refraction is highly requested after the introduction of multifocal IOLs.
Accurate refractive prediction requires good measurements of the corneal power and the axial length (AL), use of a suitable IOL calculation formula to predict the postoperative anterior chamber depth (ACD), an IOL with accurate power, and an uneventful surgery without complications. However, among these variables, it has been repeatedly emphasized that biometry is the most critical factor in obtaining the expected final refractive result.1-3
For the AL measurement, the ultrasound (US) method had been the gold standard. However, its accuracy seems to vary among operators and even among US devices.4,5 Recently, a new device for biometry, using the principle of partial coherence interferometry (PCI) has been developed. Until today, the IOL Master® (Carl Zeiss, Germany) is the only commercially available PCI device for ocular biometry. It has been well demonstrated that the IOL Master® is operator independent,5-7 highly precise, accurate, reproducible,2,6,8-11 efficient,12 and comfortable for patients.2,11,13 The IOL Master® also has an advantage over the US in that it requires no contact with the eyes, thus minimizing the risk of corneal injury and infection.5,6
It has been proposed that the IOL Master® is more likely to measure the true visual axis when the patient can maintain proper fixation during the examination.14 On the contrary, the ability to maintain proper fixation during repeated measurements
is likely to affect the accuracy and reproducibility of measurements. Factors that might affect fixation include old age, dense opacities in the ocular media, poor preoperative visual acuity, and preoperative refraction. Dense opacities in the visual axis may also cause scattering of light used for PCI
biometry.15 A low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) may indicate that the quality of the measurement is less than optimal.16,17 Although PCI biometry has become more widely used, there are only a few reports regarding the degree to which the prediction of final refraction is actually affected by the various factors listed above.15,18-20
The principal purpose of this study is to evaluate the refractive predictability of the IOL Master® for phacoemulsification cataract surgery with posterior chamber IOL implantation and to examine the effects of multiple factors on the accuracy of the refractive predictability.
A thorough chart review was conducted for patients who had undergone ocular biometry with an IOL Master® and subsequent cataract surgery at our hospital from March 2007 to December 2007. Only cases treated with an uneventful phacoemulsification surgery performed by one experienced surgeon using a self-sealing temporal clear corneal incision and a posterior chamber IOL implantation in the capsular bag were included. In all cases, I-Flex® IOLs (I-Medical®, Germany) were implanted with the manufacturer's recommended A-constant of 118.8. However, an A-constant of 118.6 was used for the IOL calculation as recommended for the IOL Master®. Exclusion criteria were as follows: patients lost from the follow-up before 5 weeks eyes with the postoperative best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) less than 0.7 (decimal scale); eyes with ocular comorbidities that could seriously affect central vision; eyes with diabetic retinopathies worse than moderate nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy or those with evidence of diabetic macular edema; or eyes with a history of other ocular surgery.
Two hundred and nine eyes from 151 patients were included in this study. In all cases, one technician (KYH) measured both the keratometric value and the AL with the IOL Master®. The exam was repeated if the recorded signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) value was too small and data were stored only if successive measurement values showed a certain degree of consistency. In suboptimal measurement cases, an asterisk (*) was recorded in the printout instead of a numerical SNR value. In such cases the SNR was defined as 1.0. The keratometric values, ALs, and the recorded SNRs were retrieved. Refraction measurements were obtained by an autokeratorefractometer and confirmed by subjective refractions. The final postoperative refraction was determined at least 5 weeks postoperatively. Collected data included: patient age, gender, and morbidity with diabetes mellitus; keratometric values, AL, and the SNR asmeasured by the IOL Master®; grade of PSC (according to the LOC III system21); preoperative VA and refraction; intended refraction with the implanted IOL; and postoperative refraction.
The prediction error was defined as the postoperative spherical equivalent (SE) minus the intended SE; its absolute value was defined as the absolute error. The mean error and the mean absolute error (MAE) were calculated using both the SRK-II and SRK/T formulas. VAs were converted to logMAR for statistical analysis.
Cases were grouped, compared,and analyzed according to gender, age, preoperative VA, preoperative refraction, degree of posterior subcapsular cataract (PSC), AL, and SNR. The Student's t-test, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and the Kruskal-Wallis test were used to compare the mean errors and the MAEs between these groups. In every statistical analysis, a p value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
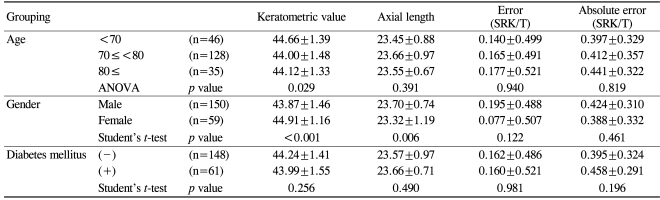
Among the 209 eyes, 150 eyes (71.8%) were from 113 males and 59 eyes (28.2%) were from 38 females. The mean age of the patients was 73.3┬▒7.2 years (range: 54-90 years). Sixty-one eyes (29.2%) were from diabetic patients. The mean time interval for postoperative refraction was 10.22┬▒4.68 weeks (range: 5.14-39.86 weeks) and the length of postoperative follow-up was 3.55┬▒2.50 months (range: 1.20-14.70 months).
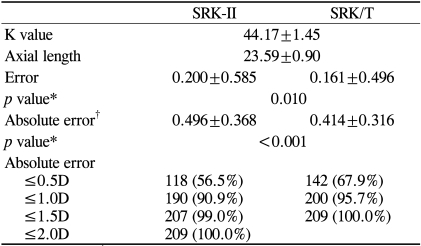
The comparison of the overall refractive predictabilities between the SRK-II and SRK/T formulas is provided in Table 1. The mean keratometric value and the mean AL for all of the cases were 44.17┬▒1.45D (range: 40.13-47.05D) and 23.59┬▒0.90 mm (range: 21.75-29.61 mm), respectively. The mean error and the MAE for the SRK-II formula were 0.200┬▒0.585D and 0.496┬▒0.368D, respectively, and 0.161┬▒0.496D and 0.414┬▒0.316D for the SRK/T formula, respectively. Both the mean error and the MAE were significantly smaller for the SRK/T formula compared to the SRK-II formula (p=0.010 and <0.001, respectively). The percentages of cases whose prediction errors were within ┬▒0.5D of the intended refraction were 51.7% for the SRK-II formula and 63.8% for the SRK/T formula, while the percentages of cases with errors within ┬▒1.0D were 86.2% for the SRK-II formula and 95.7% for the SRK/T formula. There were only two cases that had absolute errors greater than 1.5D when the SRK-II formula was used, while no cases showed an absolute error greater than 1.5D with the SRK/T formula. In general, the SRK/T formula performed better than the SRK-II formula with regard to refractive predictability.
Table 2 shows the results of the analysis of the effects of patient characteristics on the refractive predictability of the IOL Master®. The mean errors and the MAEs were not significantly affected by age, gender, or the morbidity of diabetes mellitus.
Tables 3 through 6 show the results of the analysis of the effects of certain variables that were thought to be related to the quality of the IOL Master® biometry.
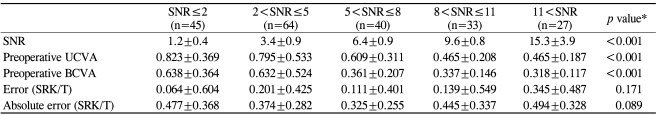
Cases were analyzed according to the SNR (Table 3). In 30 cases an asterisk (*) was marked instead of a numerical SNR value, in which case the SNR was defined as 1.0. No numerically recorded SNR was smaller than 1.6. The mean SNR for all of the cases was 6.03┬▒4.76 (range: 1.0-29.6). Cases were classified into 5 categories according to the SNR: SNRŌēż2, 2<SNRŌēż5, 5<SNRŌēż8, 8<SNRŌēż11, and 11<SNR. Low SNR values were only associated with poor preoperative VAs (p<0.001) and not with increased mean errors or MAEs (p=0.171 and 0.089, respectively). Even in the SNRŌēż2 group, the mean error and the MAE were not significantly increased.
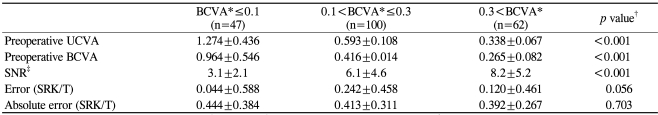
The mean preoperative BCVA for all of the cases was 0.40┬▒0.19 (0.49┬▒0.38 logMAR). Cases were grouped into 3 categories according to preoperative BCVA (decimal scale) (Table 4): preoperative BCVAŌēż0.1, 0.1<preoperative BCVAŌēż0.3, and 0.3<preoperative BCVA. Poor preoperative VAs were associated only with low SNR values (p<0.001) and not with increased errors or absolute errors (p=0.056 and 0.703, respectively).
With regard to the grade of PSC (according to the LOC III system), cases were classified into 3 groups (Table 5): P1-2 group, P3 group, and P4-5 group. Severe PSCs were significantly associated with poor preoperative VAs and poor SNRs. However, the errors and the absolute errors were not significantly affected by PSC severity (p=0.907 and 0.806, respectively).
Regarding the preoperative refraction (SE), cases were categorized into 5 groups (Table 6): SE<-4.0D, -4.0DŌēżSE<-2.0D, -2.0DŌēżSE<0.0D, 0DŌēżSE<+2.0D, and +2.0DŌēżSE. Mean hyperopic shifts in refraction were observed in all groups postoperatively with the largest hyperopic shift observed in the SEŌēź+2.0D group (the group with the most hyperopic preoperative refraction). The SEŌēź+2.0D group was also associated with the highest mean SNR. However, the MAEs were not significantly different among the groups (p=0.369). The group with a preoperative SEŌēź+2.0D was associated with the highest mean SNR and a significantly larger postoperative hyperopic shift in refraction than the other groups, but not with a significantly increased MAE.
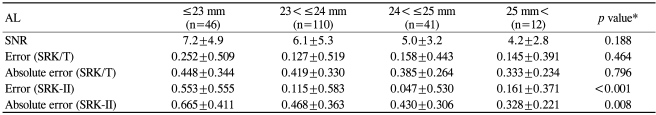
Eyes were classified into 5 groups according to AL (Table 7): ALŌēż23.0 mm, 23.0 mm<ALŌēż24.0 mm, 24.0 mm<ALŌēż25 mm, and 25 mm<AL. The group with the shortest AL (ALŌēż23.0 mm) was associated with the largest mean prediction error and MAE with the SRK-II formula, indicating the largest mean hyperopic shift in postoperative refraction in this group. However, using the SRK/T formula, the differences in mean error and MAE were not statistically significant, indicating no significant hyperopic shift in the group with ALŌēż23.0 mm.
To summarize Tables 3 through 7, poor preoperative VAs and dense PSCs were associated with poor SNR values. However, none of these, including the poor SNR values themselves, significantly affected the mean error or the MAEs. Preoperative SEsŌēź+2.0D were significantly associated with the largest mean postoperative hyperopic shift in refraction. ALsŌēż23.0 mm were also associated with the largest mean hyperopic shift in refraction, which was significant only when the SRK-II formula was used. AL was not significantly associated with the prediction error or the absolute error using the SRK/T formula.
Clinical investigations comparing the predictability of IOL power using PCI and US have been somewhat inconclusive. Some authors have shown better refractive predictability with PCI than contact US,2,3,18,22,23 while others have shown comparable results between PCI and immersion US.9,24 One previous report showed comparable refractive results between PCI and contact US.25 The refractive predictability of the IOL Master® is generally better than applanation US and equal to immersion US.
Our data showed that 63.8% and 95.7% of cases resulted in prediction errors within ±0.5D and ±1.0D, respectively. These results are comparable to those reported by Olsen26 using the IOL Master® and to Elder's report27 using applanation US. Our results are better than the result of Haigis et al.9 who reported 84.7-85.7% of cases with prediction errors within 1.0D using high definition immersion US. Our results are also better than the 36.3% of cases with prediction errors within 0.5D and the 82.7% of cases with prediction errors within 1.0D reported by Song et al.18 using the IOL Master®. The absolute error slightly increased in older patients and in patients with diabetes mellitus. However, the differences were small and not statistically significant. It is believed that the IOL Master® can provide relatively accurate and reliable measurements in these patients who may have difficulty cooperating properly for US measurement.
The relationship between cataractous opacities and the measurement outcomes seems to be somewhat complex and inconclusive. Tehrani et al.17 showed that measurement failure (17%) with the IOL Master┬« was related to lens opacity, low visual acuity, and macular disease. Freeman et al.28 reported that the failure rate for AL measurement was approximately 20% using the IOL Master┬« and that the principal cause was dense PSCs. They suggested the LOC III score of p=3.5 as the limit of PSC severity for which the IOL Master┬« can perform AL measurements. However, our study, which is based on recorded biometric data, clearly showed that the prediction error was not significantly increased in eyes with dense PSCs (pŌēź3). Hitzenberger et al.29 observed that only the SNR decreased with increasing lens density in cases without higher cataract grades and comparison of several successive scans yielded reliable results even in cases with higher cataract grades. They suggested that the reason for this good performance was related to the use of a rather long wavelength (780 nm), which caused less light scattering than a shorter wavelength. Recently, Ueda et al.20 stated that cataract density was significantly correlated with prediction error for both the IOL Master┬« and US and that the accuracy of prediction was less affected in the IOL Master┬«. They calculated the coefficients of correlation between the cataract density and the MAEs (0.24 for the IOL Master┬« and 0.29 for US) and compared them. In our study, we compared the mean prediction errors and the MAEs between different PSC groups. Our results showed that a dense PSC was not significantly associated with increased prediction error. Lee et al.13 also observed that once measurements were made with the IOL Master┬«, the measured value was not greatly affected by the type of cataract. However, it seems that controversy over the relationship between cataractous opacities and the refractive predictability of the IOL Master┬« are somewhat inevitable because the diversity of cataracts included in studies cannot be sufficiently controlled. We hope that further studies with large scale and proper stratification will more clearly delineate this issue.
Olsen and Thorwest16 compared ALs measured by US and the IOL Master┬«. They suggested that the difference in measured ALs between the two devices was minimized with SNR valuesŌēź2.1. Suto et al.15 compared the difference in pre- and postoperative ALs according to the SNR. They reported a mean decrease in AL following cataract surgery with the greatest decrease in the SNR<2.0 group and insignificant mean hyperopic shift in postoperative refraction uniquely observed in the SNR<2.0 group. However, it seems that comparison of pre- and postoperative ALs poses a problem because some authors have already reported mean AL shortening following cataract surgery.17,22,30 This phenomenon was partially explained by a slightly low group refractive index used for crystalline lenses, which is assumed to be constant for all types and intensities of cataract.16,30 In this study, we assessed the more practical effect of the SNR on the refractive predictability. Although it is possible that other factors may affect the prediction error, such as differences in capsulorhexis configuration, the actual postoperative ACD (positioning of the IOL) of individual eyes, the wound healing process, and measurement errors in the postoperative refraction, comparison of the results of refractive prediction according to various factors was thought to be more practical and meaningful than comparison of the measured ALs. Although a poor SNR was significantly related to poor preoperative VAs, we did not observe significant differences in the mean error or the MAE among the SNR groups. This result suggests that the effect of SNR on the prediction error was actually quite small and practically insignificant. Our result also showed that the eyes with the most hyperopic preoperative refraction (the group with Ōēź+2.0D in SE) were associated with significantly greater hyperopic shifts (larger prediction error) than the other groups, despite a significantly higher mean SNR value in this group. This clearly shows that a higher SNR value does not necessarily mean a smaller error in refractive prediction. Care must be taken in interpreting the significance of the SNR value. An SNR value alone may neither warrant nor exclude the validity of measurements.
Significantly greater mean hyperopic shifts in postoperative refraction were observed in eyes with preoperative SEs Ōēź+2.0D (with SRK-II and SRK/T) and ALsŌēż23 mm (with SRK-II only). Our results suggest that eyes with greater hyperopic refraction are at risk of developing significant hyperopic shifts in postoperative refraction and that shorter eyes are at the same risk when the SRK-II formula is used for the IOL power calculation. H├żsemeyer et al.19 reported that prediction error was greater for eyes with shorter ALs (AL<23.2 mm), while Song et al.18 reported that the MAE increased in eyes with longer ALs. Our result is consistent with the report by H├żsemeyer et al. and Norrby's previous observation that short eyes are more sensitive to errors, with postoperative ACD being a large contributor to error, particularly in short eyes.31 The mean group refractive index used for the entire eye may be inadequate for eyes with extreme ALs in which the lens represents too small or too large a part of the AL.24 However, because our study has shown that the refractive prediction was not significantly affected by the AL using the SRK/T formula, it is likely that selection of a suitable IOL calculation formula is important and may significantly affect the refractive prediction in eyes with extreme ALs.
There have been several reports comparing the refractive predictability of various IOL calculation formulas using the IOL Master®.22,23,32,33 In our study, the SRK/T formula performed better than the SRK-II formula, with a smaller mean error and MAE, as well as greater percentages of cases within ±0.5D and ±1.0D of the intended refraction. Table 7 shows that the SRK/T formula also treated all eyes equally well, regardless of AL. This clearly indicates that selection of an IOL calculation formula can significantly affect refractive predictability.
PCI biometry is expected to bring about huge changes in cataract surgery because of its performance in refractive prediction, operator independence, accuracy, and reproducibility. For example, PCI biometry allows surgeons around the world to compare results and exchange information regarding the most appropriate A-constant or other IOL constants.34 We hope that more accurate and objective biometry with PCI will help define and minimize other sources of error. Norrby31 recently expressed that improvements in the predictability of the IOL power calculation should focus on the three largest sources of error: estimation of postoperative IOL position, determination of postoperative refraction, and measurement of the AL. According to Norrby, the largest source of error among these three should be in the prediction of the postoperative ACD in the IOL calculation formula. Olsen34 and Preussner35 have also stated that, with PCI, the largest source of error in the IOL power calculation should no longer be the AL measurement, but rather the method used to predict the postoperative ACD, followed by keratometry. Our observations are consistent with their ideas in that the SRK/T formula generally performed better than the SRK-II formula and treated all eyes equally well, regardless of AL.
As stated above, there is a possibility that other factors could affect the final refractive results seen in our cases. These may include differences in capsulorhexis configuration, the actual postoperative ACD (positioning of the IOL) of individual eyes, differences in wound healing processes, variability of the time interval required to reach refractive stability, and errors related to the measurement of postoperative refraction. However, it seems that some of these factors are not measurable and thus are not controllable; it has also been suggested that some are inevitable.31,36 Despite these limitations, we hope that our study will provide valuable guidance in the interpretation and application of biometric data obtained by the IOL Master® in current clinical settings. We also expect that the performance and limitations of the IOL Master® will be more clearly delineated by subsequent studies, as will other undefined sources of error in refractive prediction related to cataract surgery.
Our experience with the IOL Master┬« showed fairly good results in refractive prediction for cataract surgery.31,34 Selection of a suitable IOL calculation formula is likely to improve its performance, as our study showed better overall refractive prediction with the SRK/T formula, including cases with extreme ALs. Preoperative refraction (SE)Ōēź+2.0D was significantly associated with greater hyperopic shift in postoperative refraction. Although poor preoperative VAs, dense PSCs, and poor SNR values were closely interrelated, they did not significantly affect prediction error. Our study suggests that carefully verified data from repeated measurements taken with a certain degree of consistency by the IOL Master┬« can be utilized to calculate the IOL power without significantly increasing the prediction error, regardless of the SNR, preoperative VA, the presence of dense PSCs, or the AL. We hope further studies will more clearly delineate the efficacy and limitations of the IOL Master┬« and other undefined sources of prediction errors.
REFERENCES
1. Olsen T. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg 1992;18:125-129.


2. Cannors R 3rd, Boseman P 3rd, Olson RJ. Accuracy and reproducibility of biometry using partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg 2002;28:235-238.


3. Rajan MS, Keilhorn I, Bell JA. Partial coherence laser interferometry vs. conventional ultrasound biometry in intraocular lens power calculations. Eye 2002;16:552-556.


4. Norrby S, Lydahl E, Koranyi G, Taube M. Comparison of 2 A-scans. J Cataract Refract Surg 2003;29:95-99.


5. Findl O, Kriechbaum K, Sacu S, et al. Influence of operator experience on the performance of ultrasound biometry compared to optical biometry before cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 2003;29:1950-1955.


6. Choi JH, Rho GH. The reproducibility and accuracy of biometry parameter measurement from IOL Master®. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2004;45:1665-1673.
7. Kiss B, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Biometry of cataractous eyes using partial coherence interferometry: clinical feasibility study of a commercial prototype I. J Cataract Refract Surg 2002;28:224-229.


8. Vogel A, Dick HB, Krummenauer F. Reproducibility of optical biometry using partial coherence interferometry : intraobserver and interobserver reliability. J Cataract Refract Surg 2001;27:1961-1968.


9. Haigis W, Lege B, Miller N, Schneider B. Comparison of immersion ultrasound biometry and partial coherence interferometry for intraocular lens calculation according to Haigis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmolol 2000;238:765-773.

10. Goyal R, North RV, Morgan JE. Comparison of laser interferometry and ultrasound A-scan in the measurement of axial length. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2003;81:331-335.


11. Kim HJ, Kim HJ, Joo CK. Comparison of IOL Master, A-scan and Orbscan II for measurement of axial length and anterior chamber depth. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2003;44:1519-1527.
12. Packer M, Fine IH, Hoffman RS, et al. Immersion A-scan compared with partial coherence interferometry: Outcomes analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg 2002;28:239-242.


13. Lee JT, Song JS, Kim HM. The accuracy of axial length measurement using partial coherence interferometry. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2003;44:812-817.
14. Lee AC, Qazi MA, Pepose JS. Biometry and intraocular lens power calculation. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2008;19:13-17.


15. Suto C, Sata C, Shimamura E, et al. Influence of the signal-to-noise ration on the accuracy of IOLMaster measurements. J Cataract Refract Surg 2007;33:2062-2066.


16. Olsen T, Thorwest M. Calibration of axial length measurements with the Zeiss IOLMaster. J Cataract Refract Surg 2005;31:1345-1350.


17. Tehrani M, Krummenauer F, Blom E, Dick B. Evaluation of the practicality of optical biometry and applanation ultrasound in 253 eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg 2003;29:741-746.


18. Song BY, Yang KJ, Yoon KC. Accuracy of partial coherence interferometry in intraocular lens power calculation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2005;46:775-780.
19. H├żsemeyer S, Hugger P, Jonas JB. Preoperative biometry of cataractous eyes using partial coherence laser interferometry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2003;241:251-252.


20. Ueda T, Taketani F, Ota T, Hara Y. Impact of nuclear cataract density on postoperative refractive outcome: IOL Master versus ultrasound. Ophthalmologica 2007;221:384-387.


21. Chylack LT, Wolfe JK, Singer DM, et al. The Longitudinal Study of Cataract Study Group. The lens opacities classification system III. Arch Ophthalmol 1993;111:831-836.


22. Findl O, Drexler W, Menapace R, et al. Improved prediction of intraocular lens power using partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg 2001;27:861-867.


23. Eleftheriadis H. IOL Master biometry: refractive results of 100 consecutive cases. Br J Ophthalmol 2003;87:960-963.



24. Kiss B, Findl O, Menapace R, et al. Refractive outcome of cataract surgery using partial coherence interferometry and ultrasound biometry. J Cataract Refract Surg 2002;28:230-234.


25. Hwang JS, Lee JH. Comparison of the IOL Master® and A-scan ultrasound: Refractive Results of 96 consecutive cases. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2007;48:27-32.
26. Olsen T. Improved accuracy of intraocular lens power calculation with the Zeiss IOLMaster. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2007;85:84-87.


27. Elder MJ. Predicting the refractive outcome after cataract surgery: the comparison of different IOLs and SRK-II and SRK-T. Br J Ophthalmol 2002;86:620-622.



28. Freeman G, Pesudovs K. The impact of cataract severity on measurement acquisition with the IOL Master. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2005;83:439-442.


29. Hitzenberger CK, Drexler W, Dolezal C, et al. Measurement of the axial length of cataract eyes by laser Doppler interferometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1993;34:1886-1893.

30. Prinz A, Neumayer T, Buehl W, et al. Influence of severity of nuclear cataract on optical biometry. J Cataract Refract Surg 2006;32:1161-1165.


31. Norrby S. Sources of error in intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg 2008;34:368-376.


32. Wang JK, Hu CY, Chang SW. Intraocular lens power calculation using the IOLMaster and various formulas in eyes with long axial length. J Cataract Refract Surg 2008;34:262-267.


33. Chung JK, Choe CM, You YS, Lee SJ. Biometry with partial coherence interferometry and ultrasonography in high myopes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 2006;47:355-361.
34. Olsen T. Calculation of intraocular lens power: a review. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2007;85:472-485.


Table┬Ā1
Measured values and comparison of refractive predictability between the formulas for all cases
Table┬Ā4
Effect of preoperative visual acuity on the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and refractive predictability
Table┬Ā5
Effect of PSC on preoperative visual acuity, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and refractive predictability

- TOOLS




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print