 |
 |
| Korean J Ophthalmol > Volume 33(3); 2019 > Article |
Abstract
Purpose
We sought to evaluate the distribution and characteristics of meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) and the treatment patterns for symptomatic MGD patients in South Korea.
Methods
One hundred ninety-six right eyes of 196 MGD patients were enrolled. For each patient, meibum expressibility in the central eight glands in both the upper and lower eyelids was examined. Each upper and lower eyelid was separately classified into one of the following three subtypes: nonobvious obstructive (low-delivery without lid margin abnormality), obvious obstructive (low-delivery with lid margin abnormality), and hypersecretory (high-delivery with lid margin abnormality). All treatment plans were also recorded.
Results
The mean number of expressible glands of the central eight glands in the upper eyelids (3.9 ┬▒ 2.6) was significantly higher than that in the lower eyelids (2.2 ┬▒ 2.4, p < 0.001). Obvious obstructive MGD was the most common subtype, followed by the hypersecretory and nonobvious obstructive subtypes in both the upper and lower eyelids. Of the 196 subjects, 38 (19.4%) had upper and lower eyelids that were assigned to different categories. Eyelid hygiene was the most prescribed treatment (74.5%), followed by lubricant eye drop usage (71.5%). Physicians tended to determine treatment plans based on the subtype of the upper eyelid rather than that of the lower eyelid.
Conclusions
The majority of subjects were classified as having the obvious obstructive subtype of MGD, and 19.4% had upper and lower eyelids that were different subtypes. Eyelid hygiene was the most prescribed treatment for MGD patients, and treatment patterns were mostly determined based on the subtype of the upper eyelids.
Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) was first described in 1980, and is defined as a condition of meibomian gland obstruction that is responsible for the reduced delivery of meibum to the lid margin [1]. In the 2011 International Workshop on MGD, this disorder was defined as a chronic, diffuse abnormality of the meibomian glands, commonly accompanied by terminal duct obstruction and/or quantitative or qualitative changes in meibum [2]. Alterations in tear composition in patients with MGD may result in ocular discomfort, clinically apparent inflammation, and ocular surface changes [2]. However, MGD may not always be characterized by inflammation or symptomatic irritation. Because of the broad clinical spectrum of MGD, the diagnosis and clinical manifestations of MGD have not yet been firmly defined and the classification of MGD is not standardized.
The classification scheme of MGD suggested by the International Workshop was categorization into the following two major conditions based on meibum secretion: low delivery and high delivery [2,3]. The low-delivery category is further classified into hyposecretory and obstructive (cicatricial or noncicatricial) [1,4,5,6], while the high-delivery category can be broken down into idiopathic and disease-associated, which includes seborrheic/atopic dermatitis and rosacea [5,7,8,9]. MGD may also be classified according to anatomical changes, pathophysiological changes, or the severity of disease. Previous classification systems have been consistently modified to meet the needs of both clinicians and researchers.
The prevalence of MGD as reported in previous studies varies widely, from 3.5% to almost 70%, and a much higher prevalence of MGD has been reported in Asian populations versus in Caucasian populations for reasons that are still not fully understood [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. This raises the necessity of performing a single-nation-based epidemiologic study of MGD to understand the wide-ranging manifestations of this disease.
In 2015, the Korean Meibomian Gland & Ocular Surface Study Group was launched by cornea specialists to develop a contemporary understanding of the clinical manifestations of MGD and ocular surface changes in the Korean population. In the current study, we performed a clinical study at multiple university hospitals based on a uniform case report form to analyze the distributions and characteristics of various MGD subtypes in South Korea.
This cross-sectional study was conducted between September 2016 and January 2017 at seven institutions (Korean Meibomian Gland & Ocular Surface Study Group) in South Korea. This study adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice. The protocol for this study for retrospective review of clinical records was approved by the institutional review board of Korea University Guro Hospital (2017GR0296). Written informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
MGD patients who had experienced symptoms of MGD for at least three months were included in this study. The criteria for MGD diagnosis included one or more of the following: (1) absent, viscous, or waxy white secretion upon digital expression; (2) the presence of two or more lid margin telangiectasias; and (3) the plugging of two or more gland orifices [10,12]. Each upper and lower eyelid was separately classified into one of the following three subtypes in all MGD patients: nonobvious obstructive, obvious obstructive, and hypersecretory (Table 1) [3,17]. The nonobvious and obvious obstructive subtypes belong to the low-delivery category and were diagnosed when less than five glands were expressible in the central eight glands by mild cotton swab pressure [18]. The difference between the nonobvious and obvious obstructive subtypes is that the obvious obstructive subtype includes subjects with inflammation and other signs of MGD pathology such as pouting or capping of the meibomian gland orifices, erythema, an irregular and thickened eyelid margin, telangiectasia, and dimpling or notching of the posterior eyelid margin [3,17,19], while the nonobvious obstructive subtype does not [17]. Separately, the hypersecretory subtype belongs to the high-delivery category and was diagnosed when more than five glands were expressible in the central eight glands and a large volume of lipid with quality change was released at the inflammatory eyelid margin during mild cotton swab compression [20]. Exclusion criteria included (1) the presence of any uncontrolled systemic diseases; (2) the use of contact lenses within one month of inclusion in the study; (3) a history of ocular surgery within one month of inclusion in the study; and (4) an allergy to fluorescein sodium or topical anesthetic [20,21].
All subjects completed a patient history questionnaire and the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) questionnaire. Subjects underwent an ophthalmic examination with slit-lamp biomicroscopy for observation of the meibomian gland orifices a nd eyelid margins. The right eye in each patient was selected for inclusion in this study. Clinical examinations were performed in the following order: (1) corneal staining with fluorescein sodium [22]; (2) tear film break-up time (TBUT); (3) identifying whether anterior blepharitis was present; and (4) applying mild cotton swab pressure onto the outer eyelid for evaluating meibum expressibility. All treatment plans were recorded either as type of ophthalmic or systemic medication or as another form of treatment, including eyelid hygiene and punctual plug usage.
Corneal staining was conducted with fluorescein sodium-impregnated paper strips (Haag-Sterit, Bern, Switzerland). The strips were wetted with normal saline and diluted dye was instilled into the ocular surface. After gentle blinking, the degree of corneal staining using fluorescein sodium was graded according to the Oxford scoring scheme (0-5 points) [22,23]. TBUT, the interval between blinking and the first appearance of a dry spot on the tear film, was measured three times using a stopwatch and the mean value of the three measurements was recorded to one decimal place. Both the upper and lower eyelids were observed with slitlamp biomicroscopy to check for anterior blepharitis. Lastly, both the upper and lower eyelids were gently pressed using a cotton swab to identify the number of expressible glands among the central eight glands [19].
Statistical analyses were performed using the Mann-Whitney U-test with the IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Student's t-tests, chi-squared tests, Fisher's exact tests, and one-way analysis of variance with a Tukey post-hoc analysis were performed to compare the clinical characteristics and the measurement results among subtypes and subgroups. Values were expressed as means and standard deviations. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
One hundred ninety-six eyes of 196 subjects were enrolled in this study. The mean age of all subjects was 59.4 ┬▒ 13.0 (range, 15 to 83) years. There were 119 females (60.7%) and 77 males. The mean OSDI score was 43.5 ┬▒ 22.6, the mean corneal staining grade was 1.0 ┬▒ 0.9, and the mean TBUT was 3.5 ┬▒ 1.5 seconds (Table 2).
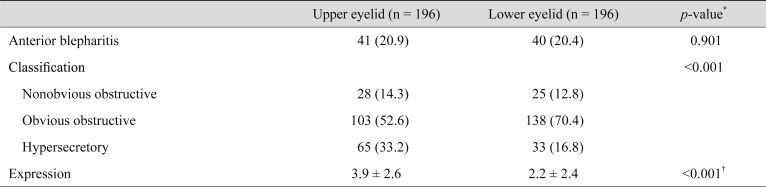
There were 41 upper eyelids (20.9%) and 40 lower eyelids (20.4%) in this study that demonstrated anterior blepharitis. Of the 196 upper eyelids of all subjects, 28 (14.3%) were classified as the nonobvious obstructive subtype, 103 (52.6%) as the obvious obstructive subtype, and 65 (33.2%) as the hypersecretory subtype, respectively. Additionally, of the 196 lower eyelids, 25 (12.8%) were classified as the nonobvious obstructive subtype, 138 (70.4%) as the obvious obstructive subtype, and 33 (16.8%) as the hypersecretory subtype. The percentage of upper eyelid cases classified as the hypersecretory subtype was significantly higher than that for the lower eyelids (p < 0.001). The mean number of glands expressible among the central eight glands in the upper eyelids was 3.9 ┬▒ 2.6, which was significantly higher than that for the lower eyelids (2.2 ┬▒ 2.4, p < 0.001) (Table 3).
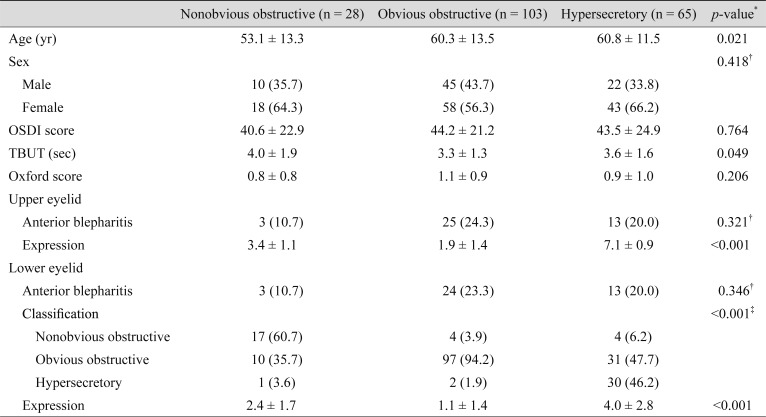
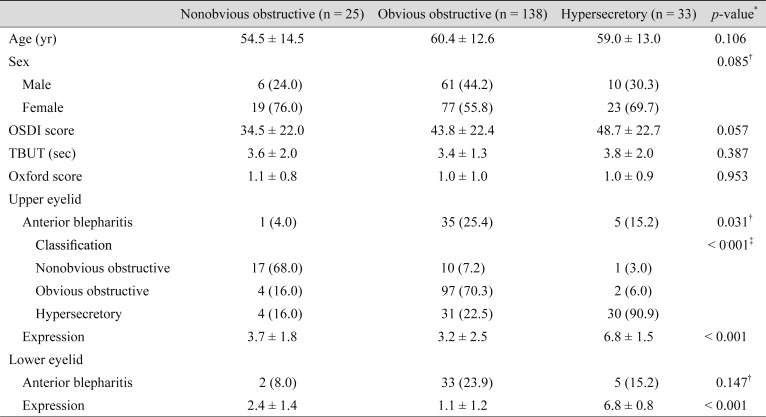
For the upper eyelids, the mean age of patients categorized as having the nonobvious obstructive subtype (53.1 ┬▒ 13.3 years) was significantly younger than that of patients categorized as having the obvious obstructive (60.3 ┬▒ 13.5 years) or hypersecretory (60.8 ┬▒ 11.5 years) subtypes (p = 0.021) (Table 4). The mean TBUT of patients with a nonobvious obstructive upper eyelid subtype (4.0 ┬▒ 1.9 seconds) was significantly greater than that of those with the obvious obstructive (3.3 ┬▒ 1.3 seconds) or hypersecretory (3.6 ┬▒ 1.6 seconds) subtypes (p = 0.049) (Table 4). On the other hand, there was no significant difference in the mean age and TBUT among the different lower eyelid subtypes (Table 5). Additionally, there was also no significant difference regarding mean OSDI score among subtypes in either the upper or lower eyelids.
Of the 196 subjects, 38 (19.4%) had different classifications (high-delivery or low-delivery) for the upper eyelid and lower eyelids, also known as mixed MGD [3]. Of the 38 cases of mixed MGD, only three patients had hypersecretory MGD in the lower eyelid; all others had hypersecretory MGD in the upper eyelid. There were no significant differences in the distribution of MGD subgroups according to whether or not MGD was accompanied by anterior blepharitis.
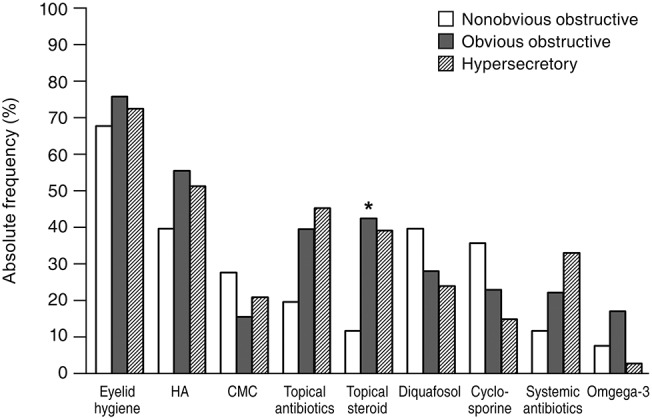
Eyelid hygiene was the most prescribed treatment (74.5%), followed by lubricant eye drops (71.4%) including hyaluronic acid (53.1%) and carboxymethylcellulose (18.4%), antibiotic (38.3%), and steroid (38.3%) eye drops. Diquafosol sodium eye drops (29.1%), cyclosporine eye drops (23.5%), systemic antibiotics (23.0%), and oral omega-3 fatty acid supplements (13.8%) were also prescribed (Fig. 1). In subtype analysis of the upper eyelids, eyelid hygiene, systemic antibiotics, and oral omega-3 fatty acid supplements tended to be prescribed more for the obvious obstructive subtype when compared with for the other subtypes. Hyaluronic acid and steroid eye drops tended to be prescribed more in the obvious obstructive and hypersecretory subtypes (Fig. 2). In subtype analysis of the lower eyelids, steroid eye drops tended to be prescribed more in the obvious obstructive and hypersecretory subtypes (Fig. 3). Of note, physicians tended to determine treatment modalities based on the upper eyelid subtype rather than that of the lower eyelid.
In this multicenter study, we evaluated the epidemiological distribution and clinical characteristics of the different MGD subtypes and the treatment patterns for MGD patients in South Korea. At first, we categorized MGD into obstructive and hypersecretory MGD. The obstructive MGD cases were further divided into obvious and nonobvious obstructive MGD according to whether inflammation and telangiectasia were present or absent on the lid margin. In this study, obvious obstructive MGD was the most common subtype observed, followed by hypersecretory and nonobvious obstructive MGD in both the upper and lower eyelids. Importantly, the MGD subtypes were not always the same in the upper and lower eyelids in the same patient. The rate of discrepancy in MGD subtype (obstructive and hypersecretory MGD) between the upper and lower eyelids in the same patient was more than 19%.
Historically, MGD has been described as a hypersecretory disorder with obvious signs of inflammation, often associated with bacterial infection [24]. In contrast, the concept of obstructive MGD, where no meibum can be expressed from the glands and the stagnation of meibum leads to reduced TBUT and superficial punctate keratopathy, has grown in importance recently [19,25,26]. Obstructive MGD is now recognized to be the most common cause of evaporative dry eye disease [25,27], and it is associated with ocular surface inflammation [2]. However, even in the first report of obstructive MGD, inflammation of the lid margin and pouting of orifices were not always present [1]. Thus, the polar concept of MGD without inflammation and purulent secretion, which was termed nonobvious obstructive MGD, was proposed by Blackie et al. [17]. Nonobvious obstructive MGD was suggested to be the precursor to obvious MGD and is thought to be significantly underdiagnosed, although the prevalence may be high. In this study, the proportion of cases of nonobvious obstructive MGD was about 12% to 14% in both the upper and lower eyelids. The mean TBUT of patients with nonobvious obstructive MGD of the upper eyelid was significantly greater than that of patients with obstructive or hypersecretory MGD. In addition, the mean age of patients with nonobvious obstructive MGD of the upper eyelid was significantly younger than that of patients with obvious obstructive or hypersecretory MGD, which supports the idea that nonobvious obstructive MGD may be an early form of meibomian gland changes.
Regarding mixed MGD, which was characterized by differences in the occurrence of obstructive and hypersecretory MGD in the upper and lower eyelids, most affected patients showed hypersecretory MGD in the upper eyelids and obstructive MGD in the lower eyelids, respectively. In addition, the overall expression of meibum was significantly greater in the upper eyelids compared with in the lower eyelids. A previous study revealed a significantly greater mean meibum grade and a significantly higher meibomian gland loss in the lower eyelids in comparison with in the upper eyelids [28]. Because upper eyelids are squeezed by mechanical muscular action, meibum is more easily and continuously secreted, with a lower chance of orifice obstruction [28]. Compensatory or complementary roles between the aqueous and lipid layers have been proposed [29,30,31]. Although defects in the aqueous and lipid layers result in dry eye disease in independent ways, these underlying mechanisms are not mutually exclusive. Likewise, obstruction of the lower eyelid may result in an increase in lipid secretion in the upper eyelid to maintain homeostasis. We could not conclude whether each subtype of MGD had an independent pathogenesis or whether all subtypes of MGD are in the line with different time positions. In either case, we suggest the observation of both the upper and lower eyelids to determine the subtype(s) of MGD present and that the treatment plan be developed based on this information.
Although obvious obstructive MGD was the most observed subtype in this study, interestingly, hypersecretory MGD with qualitative changes to meibum without orifice obstruction was more frequent in the current study versus in previous reports. It is uncertain as to whether increased secretion is a result of true hypersecretion of the glands or of a burst in the secretions due to the presence of mild obstruction. The hypersecretion of meibum could result from bacterial lipolytic exoenzymes [32], while incomplete blinking also might contribute to the pathogenesis [33,34]. A previous study hypothesized that the higher prevalence of dry eye disease and meibomian gland loss in the Asian population might be associated with blinking [33]; specifically, they showed a significantly greater proportion of participants in both the Asian single- and double-lid groups exhibited incomplete blinking as compared with those in the Caucasian double-lid group. Incomplete blinking could result in an increase in tear evaporation and ocular surface desiccation as well as a decrease in lipid flow. Poor harmonization of blinking and incorporation of lipids into the tear film can promote stagnation and an increase in the viscosity of the lipids. A previous study in Korea also showed that older female patients often had a contaminated lipid layer in which the numeric value of the lipid layer thickness was normal [35]. Thus, both qualitative and quantitative measurements of the lipid layer need to be performed in patients with MGD.
We also found that female sex was predominant in MGD patients. Sex hormones, especially androgens, are known to control the development, proliferation, and lipid production of the sebaceous glands in the entire body, and these hormones are also thought to be associated with the meibomian glands [36,37]. Androgen deficiency or postmenopausal hormone therapy are hypothesized to correlate with the occurrence of MGD [37,38]; however, there has been no report published to date that sex differences are definitively present in MGD. Because the current study only included cases of symptomatic MGD, persons who complained of ocular discomfort might be over-represented as compared with individuals with asymptomatic MGD. Further controlled studies, such as those that employ randomized sampling, are needed to analyze the presence of sex differences and the effects of sex hormones in MGD.
In this multicenter study, we found that eyelid hygiene was the most commonly prescribed treatment, and the subtype of MGD in the upper eyelid was most frequently used to guide the selection of treatment strategies. In cases of obvious obstructive or hypersecretory MGD in the upper eyelid, anti-inflammatory agents, including systemic antibiotics, omega-3 fatty acids, or topical steroids were frequently prescribed, possibly to control the inflammation on the lid margin.
This study has some limitations. First, the clinical records of patients were retrospectively reviewed. Second, this study conducted cross-sectional analysis at a single point in time, and not longitudinal analysis over a period of time. Third, this study cannot provide answers regarding the effect of treatments because this study categorized patients who were already being treated. Thus, a prospective large-scale study employing temporal and spatial observations is needed to validate the findings of this study.
In conclusion, we evaluated the distribution and characteristics of various MGD subtypes, which were classified into obstructive and hypersecretory MGD. Additionally, we analyzed the treatment patterns for MGD patients at multiple centers in South Korea. The majority of subjects were classified into the obstructive MGD subtype, and hypersecretory MGD was also a prevalent subtype in symptomatic MGD patients. The hypersecretory subtype was more frequently observed in the upper eyelid versus the lower eyelid, and the overall expression of meibum was greater in the upper eyelid. Koreans have relatively uniform genetic and environmental influences, including a mostly homogenous ethnic, climate, and food culture. Therefore, these results may be more consistent than those of other large, population-based studies. The results of this study may provide important information regarding the diverse clinical manifestations of MGD and the uncertain pathogenesis of MGD.
Notes
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
REFERENCES
1. Korb DR, Henriquez AS. Meibomian gland dysfunction and contact lens intolerance. J Am Optom Assoc 1980;51:243-251.

2. Nelson JD, Shimazaki J, Benitez-del-Castillo JM, et al. The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: report of the definition and classification subcommittee. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011;52:1930-1937.



3. Kim HM, Eom Y, Song JS. The relationship between morphology and function of the meibomian glands. Eye Contact Lens 2018;44:1-5.


4. Sirigu P, Shen RL, Pinto da Silva P. Human meibomian glands: the ultrastructure of acinar cells as viewed by thin section and freeze-fracture transmission electron microscopies. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1992;33:2284-2292.

6. Jester JV, Nicolaides N, Smith RE. Meibomian gland studies: histologic and ultrastructural investigations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1981;20:537-547.

7. Kozak I, Bron AJ, Kucharova K, et al. Morphologic and volumetric studies of the meibomian glands in elderly human eyelids. Cornea 2007;26:610-614.


8. Seifert P, Spitznas M. Immunocytochemical and ultrastructural evaluation of the distribution of nervous tissue and neuropeptides in the meibomian gland. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1996;234:648-656.


10. Viso E, Rodriguez-Ares MT, Abelenda D, et al. Prevalence of asymptomatic and symptomatic meibomian gland dysfunction in the general population of Spain. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2012;53:2601-2606.


11. Amano S, Inoue K. Estimation of prevalence of meibomian gland dysfunction in Japan. Cornea 2017;36:684-688.


12. Amano S, Inoue K. Clinic-based study on meibomian gland dysfunction in Japan. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2017;58:1283-1287.


13. Alghamdi YA, Mercado C, McClellan AL, et al. Epidemiology of meibomian gland dysfunction in an elderly population. Cornea 2016;35:731-735.



14. Siak JJ, Tong L, Wong WL, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of meibomian gland dysfunction: the Singapore Malay Eye Study. Cornea 2012;31:1223-1228.


15. Lekhanont K, Rojanaporn D, Chuck RS, Vongthongsri A. Prevalence of dry eye in Bangkok, Thailand. Cornea 2006;25:1162-1167.


16. Lin PY, Cheng CY, Hsu WM, et al. Association between symptoms and signs of dry eye among an elderly Chinese population in Taiwan: the Shihpai Eye Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005;46:1593-1598.


17. Blackie CA, Korb DR, Knop E, et al. Nonobvious obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea 2010;29:1333-1345.


18. Shimazaki J, Goto E, Ono M, et al. Meibomian gland dysfunction in patients with Sjogren syndrome. Ophthalmology 1998;105:1485-1488.


19. Foulks GN, Bron AJ. Meibomian gland dysfunction: a clinical scheme for description, diagnosis, classification, and grading. Ocul Surf 2003;1:107-126.


20. Nichols KK, Foulks GN, Bron AJ, et al. The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: executive summary. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2011;52:1922-1929.



21. Eom Y, Lee JS, Kang SY, et al. Correlation between quantitative measurements of tear film lipid layer thickness and meibomian gland loss in patients with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction and normal controls. Am J Ophthalmol 2013;155:1104-1110.


22. Eom Y, Lee JS, Keun Lee H, et al. Comparison of conjunctival staining between lissamine green and yellow filtered fluorescein sodium. Can J Ophthalmol 2015;50:273-277.


23. Bron AJ, Evans VE, Smith JA. Grading of corneal and conjunctival staining in the context of other dry eye tests. Cornea 2003;22:640-650.


24. Duke-Elder WS, MacFaul PA. The ocular adnexa. Part II. Diseases of the eyelids. In: Duke-Elder WS, MacFaul PA, System of ophthalmology. Vol. XIII. London: H. Kimpton; 1974. p. 241.
25. The definition and classification of dry eye disease: report of the Definition and Classification Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf 2007;5:75-92.


26. Lemp MA. Advances in understanding and managing dry eye disease. Am J Ophthalmol 2008;146:350-356.


27. Bron AJ, Tiffany JM. The contribution of meibomian disease to dry eye. Ocul Surf 2004;2:149-165.


28. Eom Y, Choi KE, Kang SY, et al. Comparison of meibomian gland loss and expressed meibum grade between the upper and lower eyelids in patients with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea 2014;33:448-452.


29. Goto E, Shimazaki J, Monden Y, et al. Low-concentration homogenized castor oil eye drops for noninflamed obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Ophthalmology 2002;109:2030-2035.


30. Korb DR, Greiner JV, Glonek T, et al. Effect of periocular humidity on the tear film lipid layer. Cornea 1996;15:129-134.


31. Arita R, Morishige N, Koh S, et al. Increased tear fluid production as a compensatory response to meibomian gland loss: a multicenter cross-sectional study. Ophthalmology 2015;122:925-933.


32. Dougherty JM, McCulley JP. Analysis of the free fatty acid component of meibomian secretions in chronic blepharitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1986;27:52-56.

33. Craig JP, Wang MT, Kim D, Lee JM. Exploring the predisposition of the Asian eye to development of dry eye. Ocul Surf 2016;14:385-392.


34. Wan T, Jin X, Lin L, et al. Incomplete blinking may attribute to the development of meibomian gland dysfunction. Curr Eye Res 2016;41:179-185.


35. Jung JW, Park SY, Kim JS, et al. Analysis of factors associated with the tear film lipid layer thickness in normal eyes and patients with dry eye syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2016;57:4076-4083.


36. Song JY, Kim MH, Paik JS, et al. Association between menstrual irregularity and dry eye disease: a population-based study. Cornea 2016;35:193-198.


Fig.┬Ā1
Absolute frequency of treatment modalities for patients with meibomian gland dysfunction. HA = hyaluronic acid eye drops; CMC = carboxymethylcellulose eye drops.
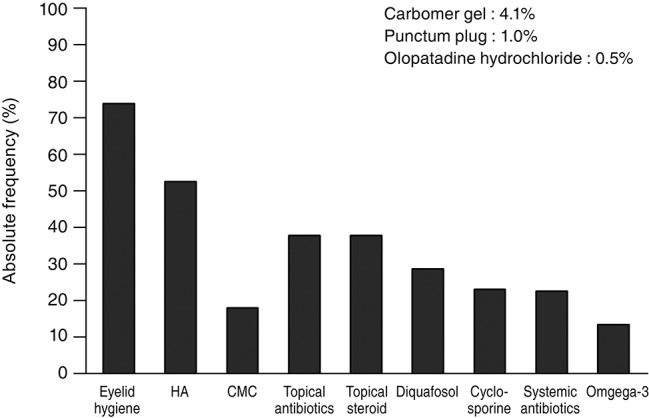
Fig.┬Ā2
Absolute frequency of treatment modalities for patients with meibomian gland dysfunction according to the subtype of the upper eyelid. HA = hyaluronic acid eye drops; CMC = carboxymethylcellulose eye drops. *p-value of less than 0.05.

Fig.┬Ā3
Absolute frequency of treatment modalities for patients with meibomian gland dysfunction according to the subtype of the lower eyelid. HA = hyaluronic acid eye drops; CMC = carboxymethylcellulose eye drops. *p-value of less than 0.05.
Table┬Ā1
Subtypes of MGD considered in this study

MGD = meibomian gland dysfunction.
*Clinically apparent inflammation and other signs of MGD pathology, such as pouting or capping of the meibomian gland orifices, erythema, an irregular and thickened eyelid margin, telangiectasia, and dimpling or notching of the posterior eyelid margin; ŌĆĀThe proportion of expressible glands of the central eight glands in the eyelid as determined by mild cotton swab pressure.




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Full text via PMC
Full text via PMC Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print